I was attempting to use pop.est to calculate abundances based on a CJS model. However, I have a few p values fixed to 0 (because there were only releases of marks, without any capture effort in those years). The function outputs NaN, presumably due to the zero variance in those years.
Is there a way to work around this?
Thank you!
Here's example code with dipper:
- Code: Select all
library(RMark)
data(dipper)
data1.proc <- process.data(dipper, model="CJS", begin.time = 2000, groups = "sex")
data1.ddl <- make.design.data(data1.proc)
## set a few p values to fixed 0
p.indices=as.numeric(row.names(data1.ddl$p[data1.ddl$p$time %in% c(2005, 2006) &
data1.ddl$p$sex == "Female",]))
p.values=rep(0,length(p.indices))
data1.analysis=function(){
Phi.1 = list(formula= ~ 1)
p.t = list(formula=~ time, fixed=list(index=p.indices, value=p.values))
cml=create.model.list("CJS")
mark.wrapper(cml,data=data1.proc, ddl=data1.ddl, output=FALSE, delete = FALSE)
}
data1.results <- data1.analysis()
md <- data1.results[[1]]
xmat <- matrix(as.numeric(unlist(strsplit(dipper$ch,""))), ncol=nchar(dipper$ch[1]))
ns <- colSums(xmat)[-1]
# calculate pop estimates
df <- data.frame(group=rep(1,6), row=c(1:6),col=c(1:6))
p.indices <- extract.indices(md,"p",df=df)
p.list <- covariate.predictions(md,data=data.frame(index=p.indices))
pop.est(ns, p.list$estimates$estimate, design=diag(1,ncol=length(unique(df$row)),nrow=length(unique(df$col))),p.list$vcv)
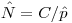 . You might be willing to assume you know something about the denominator, but you have precious little information about the numerator. You know how many newly marked individuals there are, but beyond making heroic assumptions about how many individuals might have survived from periods {1-4} -> {5} (and even that would be quite tricky), you don't have what you need to estimate abundance.
. You might be willing to assume you know something about the denominator, but you have precious little information about the numerator. You know how many newly marked individuals there are, but beyond making heroic assumptions about how many individuals might have survived from periods {1-4} -> {5} (and even that would be quite tricky), you don't have what you need to estimate abundance.